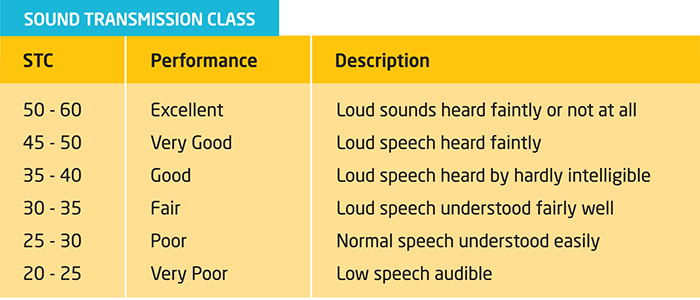
SOUND TRANSMISSION CLASS (STC) and IMPACT INSULATION CLASS (IIC)
In residential walls and ceilings by code there should be an STC of 45 or higher for partitions and floors/ceilings separating living units from other living units, public spaces, and service areas.
2 Types of Sound Transfer with Solutions to buffer sound transfer:
- (STC) SOUND TRANSMISSION CLASS
Airborne Sound Solutions for Existing Structures- TV, talking, etc.- Caulk and seal all penetrations. An amazing amount of airborne sound can get thru tiny openings.
- Ceiling fixtures should be surface mounted, not recessed, to reduce penetrations.
- It is incorrect to assume that higher density insulation means improved sound insulation. Tests have shown that insulation thickness is the most important property when describing a cavity sound absorbing material. Thickness affects the sound transmission loss at most frequencies and therefore affects the STC rating.
- IMPACT INSULATION CLASS (IIC)
Impact Sound Solutions for sound traveling a path through solid structure such as hearing your neighbor walk in the unit above. In existing buildings this is the most common and the most difficult to fix.- Cushioning the impact with carpet and pad is one of the most effective methods of isolating impact noise.
- Increase the sound insulation to treat both airborne and impact sound with the the use of fiber glass insulation with a resilient ceiling attachment. McGill Place ceilings were built with Resilient Furring Channel ceiling attachments, see guide below.
Here is a GUIDE with building details to create various STCs: WALLS_Guide for Residential Sound Control